
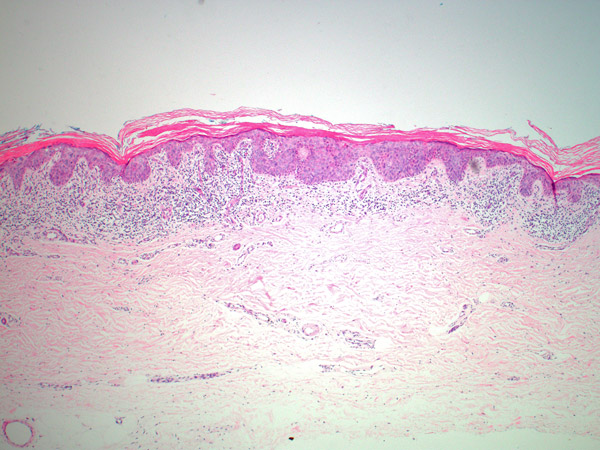
The malignant cells are confined to the epidermis, the outer layer of the skin. Bowen’s disease can precede invasive squamous cell carcinomas which can invade the skin deeply and may spread.
Bowen’s disease usually presents as a red, scaly patch. However due to the fact that its appearance can vary, a biopsy is usually performed to confirm the diagnosis.
As with other forms of skin cancer, Bowen’s disease is mainly caused by chronic sun exposure and aging. The site, size and age of the patient dictates treatment, but the most common treatment for Bowen’s disease is surgical excision - wide local excision or Mohs micrographic surgery - followed by skin surveillance by Dr Banky. Bowen’s disease can be removed by several other methods including; cryosurgery, curettage and diathermy, topical chemotherapeutic agents, PDT and laser destruction.


 03 9519 9500
03 9519 9500