
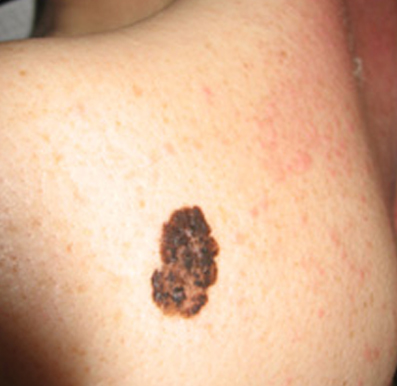
Usually asymptomatic, it presents as a changing or new pigmented lesion, often on sun-exposed sites.
Melanoma risk increases with exposure to UV radiation, particularly with episodes of sunburn or solarium use.
Also at risk are people who have increased numbers of atypical naevi, depressed immune systems, family history of melanoma, fair skin, and individuals who have had previous melanoma.
Melanoma can be diagnosed using the ABCDE method :
Asymmetry
Border irregularity
Colour variation
Diameter (usually over 6mm)
Evolving (changing and growing larger).
Diagnosis is by biopsy to remove the whole lesion, or less commonly by a punch biopsy or shave biopsy of a part of the lesion.

Surgery - wide local excision only is the mainstay of treatment for both thick (invasive) and thin (in situ) melanomas. Individuals who have had one melanoma are at risk of developing another melanoma and require ongoing skin surveillance by Dr Banky.



 03 9519 9500
03 9519 9500